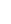
Maths
Intent
Career Opportunities in Maths
Year 7 Curriculum Overview
Autumn Term
| What are we learning? | What knowledge, understanding and skills will we gain? | What will excellence look like? | How will we recognise progress? |
|
Number Sense and Calculations
Expressions and Equations Measures |
Adding and Subtracting
Multiplying
Dividing
Calculating with Negative Numbers
Order of Operations
Expressions
Substitution
Solving Equations
Time
Measure |
Being able to round to place value and decimal places.
Understand various methods for making simple addition/subtraction calculations.
Be able to use number facts to make multiplication and division easier.
Understand that numbers extend into the negative and be able to use these in calculations.
Be able to apply the order of operations correctly.
Understand that order of operations is a fundamental rule for all questions.
Develop an understanding of algebra with regards to notation.
Be able to replace unknown values with an assigned value.
Be able to use knowledge of number sense, and order of operations, to solve simple equations. Be able to convert between units of time and understand how to use time in calculations.
Know and understand the connections between basic units of length, mass and capacity. |
These units will be assessed using formative assessment in class.
Weekly homework tasks will be set for students to complete online. The end of term assessment will be marked by the teacher, and recorded centrally, for monitoring progress. |
Spring Term
| What are we learning? | What knowledge, understanding and skills will we gain? | What will excellence look like? | How will we recognise progress? |
| 2D Shapes | Line properties Shape properties Symmetry |
Students will be able to identify parallel and perpendicular lines and use the notation for these and equal length lines (including shapes with more than one of these). They will also be able to explain a shape’s properties from this information. Students will also be able to identify different types of triangle, quadrilateral or polygon and use appropriate terminology to describe or identify the shape. They will also be able to identify regular and irregular polygons as well as correctly name these shapes given the number of sides. Students will also have an understanding of line symmetry and rotational symmetry. | These units will be assessed using formative assessment in class. Weekly homework tasks will be set for students to complete online. The end of term assessment will be marked by the teacher, and recorded centrally, for monitoring progress. |
| Perimeter and Area | Finding the perimeter using grids Finding the perimeter of rectangles and simple shapes Finding the perimeter of compound shapes Finding areas using gridsFinding the area of rectangles Finding the area of compound shapes Finding the area of triangles Finding the area of compound shapes using triangles |
Students will be able to find the perimeter or area of a range of shapes based on rectangles, triangles or a combination of one or more of these shapes. Students will be able to perform perimeter and area calculations both by using grids or by using dimensions provided. Students will be able to perform reverse calculations to find missing dimensions in such shapes when the perimeter or area is given. | These units will be assessed using formative assessment in class. Weekly homework tasks will be set for students to complete online. The end of term assessment will be marked by the teacher, and recorded centrally, for monitoring progress. |
| Coordinates | Reading and plotting coordinates Solving shape problems involving coordinates |
Students will be able to plot or read the coordinates of any point across the four quadrants of a graph. Students will be able to read and plot coordinates on a graph where the scale is not 1. Students will also be able to complete a set (or multiple sets) of coordinates to create triangles and simple quadrilaterals. They will also be able to calculate the perimeter or area of such shapes. | These units will be assessed using formative assessment in class. Weekly homework tasks will be set for students to complete online. The end of term assessment will be marked by the teacher, and recorded centrally, for monitoring progress. |
| Factors, Multiples and Primes | Finding the lowest common multiple Finding factors and using divisibility tests Finding the highest common factor Finding prime numbers Prime factor decomposition |
Students will be able to list the multiples of a given number or to identify if a number if a multiple of another number. They will also be able to find common, and the lowest common, multiple (LCM), of two or three numbers as well as understand the practical meaning of the LCM in worded problems. Students will also be able to work out factors of a given number and how to find common, and the highest common, factor of a given number. They will also understand the practical meaning of the HCF in worded problems. Students will also be able to use simple divisibility tests to identify numbers that have 2, 3, 5, 9 and 10 as factors. Students will be able to identify if a number is prime (or not prime), be able to explain why 1 is not prime, as well as to be able to write any number as a product of its prime factors (both in expanded form and index form). | These units will be assessed using formative assessment in class. Weekly homework tasks will be set for students to complete online. The end of term assessment will be marked by the teacher, and recorded centrally, for monitoring progress. |
| Fractions | Finding fractions of shapes Constructing fractions Finding equivalent fractions Simplifying fractions Ordering fractions Converting between mixed numbers and improper fractions Adding and subtracting fractions Adding and subtracting mixed numbers |
Students will be able to express a fraction as an equivalent fraction with either a different denominator or numerator. They will also be able to simplify fractions (recognising the difference between partially simplifying and fully simplifying). Students will be able to order fractions by writing a list of fractions out as improper fractions with the same denominator. Students will also be able to convert between improper fractions and mixed numbers and, by ensuring the fractions have the same denominators, add or subtract any given improper fraction or mixed number. | These units will be assessed using formative assessment in class. Weekly homework tasks will be set for students to complete online. The end of term assessment will be marked by the teacher, and recorded centrally, for monitoring progress. |
| Brackets | Using the distributive law Expanding single brackets Expanding single brackets and simplifying expressions Factorising into one bracket |
Students will be able to use to distributive law to break down complex calculations into simpler calculations. Students will also be able to expand single brackets and, where required, collect any like terms to simplify the resulting expression. Students will also be able to identify the highest common factor in an expression and use this to factorise an expression into a single bracket (and to recognise the difference between partially factorising and fully factorising). | These units will be assessed using formative assessment in class. Weekly homework tasks will be set for students to complete online. The end of term assessment will be marked by the teacher, and recorded centrally, for monitoring progress. |
Summer Term
| What are we learning? | What knowledge, understanding and skills will we gain? | What will excellence look like? | How will we recognise progress? |
| Angles |
Recognise types of angles Be able to estimate angles Be able to measuring angles Be able to draw angles
Understand that angles on a line always sum to 1800 Understand that angles about a point always sum to 3600 Understand that vertically opposite angles are always the same size Understand that the angles in triangles always sum to 1800 |
Be able to identify acute, obtuse, reflex and right angles. Be able to estimate the size of an angle. Be able to use a protractor to effectively draw and measure an angle. Be able to use angle facts to calculate missing angles within a diagram or shape. Be able to calculate the size of an unknown angle in scalene, right angled and isosceles triangles. Be able to solve problems involving angles by applying skills learned throughout this topic. Be aware of real world applications of angles. |
These units will be assessed using formative assessment whilst being delivered. Weekly homework on Sparx website. Post knowledge check will be used at the end of unit assessment, this will be marked by the student and teacher. The teacher will give feedback and set personalised task for the students to complete. There will be an end of year assessment in the first week back after the May half term.
|
| Handling Data and Statistical Diagrams |
Calculating the range Calculating the median Finding the mode Calculating the mean
Interpreting frequency tables and two-way tables Drawing and interpreting tally charts Drawing and interpreting pictograms Drawing bar charts Interpreting bar charts
Collecting and recording data using tables Finding averages from frequency tables Choosing suitable averages and solving problems
Collecting and recording data using tables Finding averages from frequency tables Choosing suitable averages and solving problems |
Be able to find the maximum and minimum values and using these to calculate the range. Be able to calculate the mean mode median and range of a list of integers. Measures context: Be able to calculate the range of a list of decimals. Temperature context: Be able to calculate the range where some values are negative. Be able to problem solve by working backwards from the mean, mode, median and range to find missing items in a data set. Be able to interpret a frequency table containing qualitative or quantitative data. Be able to calculate the mean, mode, median and range from a frequency table. Be able to read values and totals from a two-way table. Be able to find missing values in a two-way table. Be able to construct and interpret a tally chart. Be able to construct and interpret a pictogram. Be able to construct and interpret a bar chart, a dual bar chart and a composite bar chart. Be able to solve problems involving handling data and statistical diagrams by applying skills learned throughout this topic. Be aware of real world applications of handling data and statistical diagrams. | |
| Handling Data and Statistical Diagrams |
Calculating the range Calculating the median Finding the mode Calculating the mean
Interpreting frequency tables and two-way tables Drawing and interpreting tally charts Drawing and interpreting pictograms Drawing bar charts Interpreting bar charts
Collecting and recording data using tables Finding averages from frequency tables Choosing suitable averages and solving problems
Collecting and recording data using tables Finding averages from frequency tables Choosing suitable averages and solving problems |
Be able to find the maximum and minimum values and using these to calculate the range. Be able to calculate the mean mode median and range of a list of integers. Measures context: Be able to calculate the range of a list of decimals. Temperature context: Be able to calculate the range where some values are negative. Be able to problem solve by working backwards from the mean, mode, median and range to find missing items in a data set. Be able to interpret a frequency table containing qualitative or quantitative data. Be able to calculate the mean, mode, median and range from a frequency table. Be able to read values and totals from a two-way table. Be able to find missing values in a two-way table. Be able to construct and interpret a tally chart. Be able to construct and interpret a pictogram. Be able to construct and interpret a bar chart, a dual bar chart and a composite bar chart. Be able to solve problems involving handling data and statistical diagrams by applying skills learned throughout this topic. Be aware of real world applications of handling data and statistical diagrams. | |
| Proportion |
Solving proportion problems |
Be able to use multiplication to find an amount when given a unitary proportional relationship. Be able to use division to find a unitary amount when given a proportional relationship. Be able to use multiplication to find an amount when given a proportional relationship. Be able to use division to find an amount when given a proportional relationship. Be able to use a unitary method to find an amount when given a proportional relationship. Be able to interpret a recipe and using a unitary method to solve proportion problems | |
| Fractions, Decimals and Percentages |
Reciprocals Multiplying fractions Dividing fractions Fractions of amounts Converting between fractions, decimals and percentages. Ordering fractions, decimals and percentages Writing numbers as percentages of other numbers
|
Be able to write the reciprocal of a number or fraction. Multiply and divide fractions including mixed numbers. Calculate a fraction of an amount with and without a calculator. Be able to convert a decimal with one decimal place to a fraction. Be able to convert between fractions, decimals and percentages. Be able to order a list of fractions, decimals and percentages. Be able to write a number as a percentage of another number. | |
| Probability |
Using probability phrases Writing probabilities as fractions Writing probabilities as fractions, decimals and percentages Probabilities of mutually exclusive events Sample space diagrams |
Be able to understand the probability scale in words, decimals and fractions. Be able to write the probability of a single event as a fraction, decimal or percentage. Be able to interpret a written context to calculate the probability of a single event. Be able to find the probability from a frequency table. Be able to calculate the probability of an event by considering outcomes greater or less than a number and linking to a probability scale. Be able to compare probabilities given as a mix of fractions, decimals and percentages. Be able to recognise whether two events are mutually exclusive. Be able to calculate the probability of an event not happening as a fraction, decimal or percentage. Be able to complete a sample space diagram for two events. Be able to work out probabilities from a sample space diagram with a small number of outcomes. |
Year 8 Curriculum Overview
Autumn Term
| What are we learning? | What knowledge, understanding and skills will we gain? | What will excellence look like? | How will we recognise progress? |
|
Percentages and money
Algebra Ratio |
Percentages of amounts
Increase and decrease by a percentage with and without a calculator
Reverse percentages (most able students)
Value for money
Best buy
Indices
Solving Equations
Sequences
Write and simplify a ratio
Equivalent ratios
Write a ratio in the form 1:n
Convert between a ratio, fraction and percentage
Share into a ratio |
Understand that percentage means per 100
Will be able to choose the most effective method to easily and quickly find a percentage
Understand the different terminology that can be used to describe an increase or a decrease.
Able to identify when a problem is dealing with reverse percentages
Able to solve problems involving percentages, value for money and best buys
Be able to use index laws to simplify expressions involving multiplication, division and powers with indices within the terms.
Be able to use knowledge of number sense, and order of operations, to solve 1 and 2 step equations.
Be able to solve equations that involve fractions, including the unknown within the denominator
Be able to solve equations involving brackets.
To be fully fluent students will be able to construct and solve equations based on worded problems
Students will be able to find term to term rule and continue a sequence
Students will be able to find the nth term (position to term rule) and use it to find terms in the sequence
Students will be able to rewrite a worded problem as ratio and simplify this
Students will be able to use equivalent ratio to solve problems involving money.
Able to simplify a ratio that involves mixed units of measure
Are able to understand the use of the ratio 1:n including within maps.
Students will be able to effectively convert between a fraction, percentage and ratio
Students will be able to problem solve in order to identify a persons share in a ratio. |
These units will be assessed using formative assessment in class.
Weekly homework tasks will be set for students to complete online. The end of term assessment will be marked by the teacher, and recorded centrally, for monitoring progress. |
Spring Term
| What are we learning? | What knowledge, understanding and skills will we gain? | What will excellence look like? | How will we recognise progress? |
| Rounding | Rounding integers using significant figures Rounding decimals using significant figures Estimating calculations |
Students will be able to round integers and decimals to a given number of significant figures as well as be able to round decimals less than 1 (and to be able to recognise that first non zero digit is the first significant figure). Students will be able to round all calculations to one significant figure to estimate calculations. They will also appreciate the difference between calculating and estimating as well as be able to perform calculations to check that answers seem reasonable. | These units will be assessed using formative assessment in class. Weekly homework tasks will be set for students to complete online. The end of term assessment will be marked by the teacher, and recorded centrally, for monitoring progress. |
Summer Term
| What are we learning? | What knowledge, understanding and skills will we gain? | What will excellence look like? | How will we recognise progress? |
| Linear graphs |
Plotting horizontal, vertical and diagonal lines; Plotting straight line graphs; Finding equations of straight line graphs |
Students will be able plot, and draw, straight lines from an equation and recognise the equations of horizontal and vertical lines.
Students will be able to plot, and draw straight lines from equations in the form y = mx + c or zx + by + c = 0
Students will be able to find the gradient of any straight line (identifying if the gradient is positive or negative) and use this, combined with the y-intercept, to form the equation of the line in the form y = mx + c |
These units will be assessed using formative assessment whilst being delivered. Weekly homework on Sparx website.. Post knowledge check will be used at the end of unit assessment, this will be marked by the student and teacher. The teacher will give feedback and set personalised task for the students to complete. There will be an end of year assessment in the first week back after the May half term.
|
| Transformations |
Translations; Reflection |
Students will build on knowledge of reading and plotting coordinates to allow them to perform translations and reflections of varying 2 dimensional shapes.
Students will be able to accurately describe reflections and translations using appropriate mathematical terminology including the equation of the line of reflection or a column vector to describe the translation. Students will understand and be able to explain why shapes that are reflected or translated remain congruent. |
|
| Angles |
Angles in quadrilaterals; Combining angle facts; Angles on parallel lines; Using quadrilateral properties to find angles; Angles in polygons |
Students will build on the core knowledge that: The angles on a straight line sum to 180 degrees; The angles about a point sum to 360 degrees; That vertically opposite angles are equal; That the angles in a triangle sum to 180 degrees
to solve more sophisticated problems. These include:
Being able to explain why the sum of the interior angles of a quadrilateral sum to 360 degrees by splitting the shape into two triangles; Applying the core knowledge and the fact that the interior angles of a quadrilateral sum to 360 degrees to more complex problems that require using two or more of these facts; Finding the sum of the interior angle of any polygon by considering how many triangles the shape can be split up into; Finding the interior angle of any regular polygon; Using the properties of quadrilaterals (such as the opposite angles in a parallelogram) to solve angle problems; Finding the size of angles which lie on parallel lines and to be able to describe the terms ‘corresponding’, ‘alternate’, and ‘co-interior’ angles; |
|
| Statistical diagrams |
Drawing pie charts; Interpreting pie charts; Drawing line graphs; Interpreting line graphs; Drawing stem and leaf diagrams; Interpreting stem and leaf diagrams; Finding averages from diagrams |
Students will be able to choose the appropriate graph or chart to represent data and then draw the relevant diagram and interpret and critique the diagram appropriately.
Students will also be able to create and use stem and leaf diagrams to represent larger data sets and use these to find averages. |
|
| Inequalities |
Reading and drawing linear inequalities on number lines; Solving single inequalities |
Students will build on the core knowledge of using number lines, solving one step equations and two step equations.
Students should then be able to represent a single or double inequality using a number line (and write an inequality for a representation on a number line) as well as being able to solve single inequalities (including those with negative values). |
|
| Brackets |
Expanding double brackets |
Students will be able to expand a pair of double brackets including looking at special cases such as the difference of two squares and expressions in the form (x±y)2.
Students will also be able to ensure their answers are simplified by collecting like terms. |
|
| Algebraic fractions |
Calculating with fractions; Calculating with mixed numbers; Simplifying algebraic fractions by factorising; Adding and subtracting algebraic fractions
|
Students will recap the key operations with fractions (using both improper fractions and mixed numbers) and then use the same skills and methodology to apply these skills to algebraic fractions.
Students will also be able to simplify operations with algebraic fractions by factorising expressions so that like expressions can be cancelled out. |
|
| Recurring decimals |
Using recurring decimal notation; Converting fractions to recurring decimals |
Students will be able to accurately write a recurring decimal using the ‘recurring dot’. They will also be able to convert any fraction into a recurring decimal. |
Year 9 Curriculum Overview
Autumn Term
| What are we learning? | What knowledge, understanding and skills will we gain? | What will excellence look like? | How will we recognise progress? |
|
Fractions, decimals and percentages Percentage change |
Understand that a multiplicative relationship between two quantities can be expressed as a ratio or a fraction Solve problems involving percentage change, including: percentage increase, decrease and original value problems and simple interest in financial mathematics. |
Apply fundamentals of fractions, decimals and percentages to solve problems in the context of the wider world.
|
These units will be assessed using formative assessment whilst being delivered. Weekly homework on Sparx website, GCSE exam questions will be used within lessons. Post knowledge check will be used at the end of unit assessment, this will be marked by the student and teacher. The teacher will give feedback and set personalised task for the students to complete.
|
| Theoretical and experimental probabilities and frequency tree. | Students will learn to calculate the probability of combined events, mutually exclusive events, experimental probability and independent events. Students will learn to use frequency trees. | Students will be able to solve a variety of complex probability problems including independent and dependent events. They will be able to use solving real life probability problems. | These units will be assessed using formative assessment whilst being delivered. Weekly homework on Sparx website, GCSE exam questions will be used within lessons. Post knowledge check will be used at the end of unit assessment, this will be marked by the student and teacher. The teacher will give feedback and set personalised task for the students to complete. |
| Calculation with standard form |
Students will learn writing large and small numbers in standard form by multiplying and dividing numbers in standard form and adding and subtracting numbers in standard form. They will also learn how to do calculations using standard form on your calculator. |
Students able to change ordinary numbers to standard form and vice versa. Students able to write both small and large numbers in standard form and use them in calculation relating to real life problems. |
These units will be assessed using formative assessment whilst being delivered. Weekly homework on Sparx website, GCSE exam questions will be used within lessons. Post knowledge check will be used at the end of unit assessment, this will be marked by the student and teacher. The teacher will give feedback and set personalised task for the students to complete. |
| Linear inequalities |
Students will learn how to solve inequalities with the unknown on both sides and solve double inequalities. They will learn how to construct and solve inequalities. |
Students able to solve inequalities |
These units will be assessed using formative assessment whilst being delivered. Weekly homework on Sparx website, GCSE exam questions will be used within lessons. Post knowledge check will be used at the end of unit assessment, this will be marked by the student and teacher. The teacher will give feedback and set personalised task for the students to complete. |
| Factorising and solving quadratic equations |
Students will learn how to factorise quadratic equations of the form , factorise the difference of two squares and factorise to solve quadratic equations. |
Students will also be able to calculate fluently and solve problems in context using all of the skills gained. Students will also be able to apply these algebraic techniques to solve worded and geometrical problems. |
These units will be assessed using formative assessment whilst being delivered. Weekly homework on Sparx website, GCSE exam questions will be used within lessons. Post knowledge check will be used at the end of unit assessment, this will be marked by the student and teacher. The teacher will give feedback and set personalised task for the students to complete. |
Spring Term
| What are we learning? | What knowledge, understanding and skills will we gain? | What will excellence look like? | How will we recognise progress? |
| Rounding | Finding error intervals Truncating decimals Finding error intervals for truncated numbers |
Students will progress to finding bounds for calculations | These units will be assessed using formative assessment whilst being delivered. Weekly homework on Sparx website, GCSE exam questions will be used within lessons. Post knowledge check will be used at the end of unit assessment, this will be marked by the student and teacher. The teacher will give feedback and set personalised task for the students to complete. |
| Pythagoras Theorem | Using and applying by Pythagoaras Theorem to 2D shapes | Students will progress to using to applying Pythagoras to 3D shapes as well as other questions involving Right Angled Trigonometry | These units will be assessed using formative assessment whilst being delivered. Weekly homework on Sparx website, GCSE exam questions will be used within lessons. Post knowledge check will be used at the end of unit assessment, this will be marked by the student and teacher. The teacher will give feedback and set personalised task for the students to complete. |
| Ratio and Proportion | Solving direct proportion word problems Solving inverse proportion word problems Currency conversion |
Students who are excelling at this topic will progress onto topics such as Combining ratios, Calculating with ratios and algebra, Changing ratios,Interpreting direct proportion equations, Interpreting inverse proportion equations | These units will be assessed using formative assessment whilst being delivered. Weekly homework on Sparx website, GCSE exam questions will be used within lessons. Post knowledge check will be used at the end of unit assessment, this will be marked by the student and teacher. The teacher will give feedback and set personalised task for the students to complete. |
| Linear Graphs | Plotting straight line graphs Finding equations of straight line graphs Interpreting equations of straight line graphs |
Students who are achieving excellence will explore topics such as Equations of parallel lines, Finding the equation of a straight line from its gradient and a point, Finding the equation of a straight line from two points on the line | These units will be assessed using formative assessment whilst being delivered. Weekly homework on Sparx website, GCSE exam questions will be used within lessons. Post knowledge check will be used at the end of unit assessment, this will be marked by the student and teacher. The teacher will give feedback and set personalised task for the students to complete. |
| Compound Measures | Calculating with speed Calculating with rates |
Students who are achieving excellence will explore further topics related to Density, Mass and Volume as well as Pressure, Force and Area | These units will be assessed using formative assessment whilst being delivered. Weekly homework on Sparx website, GCSE exam questions will be used within lessons. Post knowledge check will be used at the end of unit assessment, this will be marked by the student and teacher. The teacher will give feedback and set personalised task for the students to complete. |
| Motion Time Graphs | Interpreting distance-time graphs Calculating speed from distance-time graphs Plotting distance-time graphs using speeds |
Students who are achieving excellence will progress on to plotting velocity time graphs. | These units will be assessed using formative assessment whilst being delivered. Weekly homework on Sparx website, GCSE exam questions will be used within lessons. Post knowledge check will be used at the end of unit assessment, this will be marked by the student and teacher. The teacher will give feedback and set personalised task for the students to complete. |
Summer Term
| What are we learning? | What knowledge, understanding and skills will we gain? | What will excellence look like? | How will we recognise progress? |
| Quadratic Graphs |
Plotting quadratics Interpreting quadratics Solving quadratics graphically |
Students will be able to generate a table of values to plot a quadratic function. They will understand the terminology used to describe a quadratic and will be able to find the roots of a quadratic equations from its graph. |
These units will be assessed using formative assessment whilst being delivered. Weekly homework on Sparx website, GCSE exam questions will be used within lessons. Post knowledge check will be used at the end of unit assessment, this will be marked by the student and teacher. The teacher will give feedback and set personalised task for the students to complete. There will be an end of year assessment in the first week back after the May half term.
|
| Angles and Bearings |
Angles Combining angle facts Angles in parallel lines Angles in quadrilaterals Angles in polygons Bearings Measuring and drawing bearings Calculating bearings |
Students will be able to identify which angle rule applies to a question and use it effectively. Students will combine angle facts in order to solve multi-step problems and give reasons for each stage of their working. Students will be able to effectively use a protractor to measure and draw bearings. They will be able to use angle facts to calculate bearings from diagrams. | |
| Transformations |
Translations Reflections Rotations Enlargement by a positive scale factor |
Students will be able to translate, reflect, rotate and enlarge shapes on a coordinate axis from given directions. Students will be able to identify and describe transformations based on a diagram. Students will be able to perform multi-step transformations and describe the result as a single transformation. | |
| Similarity and Congruence |
Similarity Understanding similarity Finding unknown sides in similar shapes Congruence Understanding congruence Congruent triangles Constructing triangles |
Students will be able to identify similar shapes and calculate scale factors. Students will use scale factors to find missing lengths in similar shapes and use similarity to problem solve. Students will be able to define congruence and identify congruent shapes. Students will know and identify the rules for proving congruent triangles. Students will accurately use a ruler and protractor to construct triangles. | |
| Data and Statistical Diagrams |
Scatter Graphs Plot Interpret Lines of best fit Collect and represent data Types of data Presenting data and making conclusions Comparing populations using diagrams Choosing suitable averages and solving problems Grouped data Interpreting frequency tables with grouped data Finding averages Draw and interpret frequency polygons |
Students will accurately plot coordinates from a table of values to create a scatter graph. Students will be able to identify the correlation of a scatter graph and describe the relationship between two variables in real terms. Students will be able to accurately draw a line of best fit and use this to estimate results. Students will know the definition of qualitative data, quantitative data. discrete data, continuous data, primary data and secondary data. Students will identify the best chart or graph to depict a set of data. Students will interpret pie chart, line graphs and stacked bar charts. Students will calculate the mean, mode, median and range from a set of grouped data. Students will accurately plot and interpret frequency polygons. |
|
| Vectors |
Understand what a column vector is Add and subtract column vectors Multiply a column vector by a scalar Identify parallel vectors |
Students will use column vector notation to describe a movement. Students will accurately draw diagrams to describe column vectors. Students will add and subtract column vectors as diagrams and in notation, they will also multiply column vectors by a scaler as diagrams and in notation. |
Year 10 Curriculum Overview
Autumn Term
| What are we learning? | What knowledge, understanding and skills will we gain? | What will excellence look like? | How will we recognise progress? |
|
Algebra
|
All students will:
Higher tier students will:
|
Confidence in applying skills in independent practise leading to problem solving skills with links to other areas of maths with a focus on geometry.
|
These units will be assessed using formative assessment whilst being delivered. Weekly homework on Sparx website, GCSE exam questions will be used within lessons. Post knowledge check will be used at the end of unit assessment, this will be marked by the student and teacher. The teacher will give feedback and set personalised task for the students to complete. |
| Probability |
All students will:
Higher tier students will:
|
Students will be able to solve a variety of complex probability problems including independent and dependent events. They will be able to use solving real life probability problems.
|
These units will be assessed using formative assessment whilst being delivered. Weekly homework on Sparx website, GCSE exam questions will be used within lessons. Post knowledge check will be used at the end of unit assessment, this will be marked by the student and teacher. The teacher will give feedback and set personalised task for the students to complete. |
| Congruent and similarity |
All students will:
Higher tier students will:
|
Students will be able to identify congruent shapes and explain their relationship. They will also understand where similarity and congruence is used in real life.
|
These units will be assessed using formative assessment whilst being delivered. Weekly homework on Sparx website, GCSE exam questions will be used within lessons. Post knowledge check will be used at the end of unit assessment, this will be marked by the student and teacher. The teacher will give feedback and set personalised task for the students to complete. |
| Multiplicative reasoning |
All students will:
Higher tier students will: Algebraic direct and inverse proportion |
Students will relate these skills to real life problem solving. Those who have mastered the topic will be able to problem solve with links to geometric questions.
|
These units will be assessed using formative assessment whilst being delivered. Weekly homework on Sparx website, GCSE exam questions will be used within lessons. Post knowledge check will be used at the end of unit assessment, this will be marked by the student and teacher. The teacher will give feedback and set personalised task for the students to complete. |
Spring Term
| What are we learning? | What knowledge, understanding and skills will we gain? | What will excellence look like? | How will we recognise progress? |
| Multiplicative Reasoning | All students will: Calculate percentages Increase and decrease by a percentage Calculate distant, speed and time Calculate numerical direct and inverse proportion questions |
Students will relate these skills to real life problem solving. Those who have mastered the topic will be able to problem solve with links to geometric questions. | These units will be assessed using formative assessment whilst being delivered. Weekly homework on Sparx website, GCSE exam questions will be used within lessons. Post knowledge check will be used at the end of unit assessment, this will be marked by the student and teacher. The teacher will give feedback and set personalised task for the students to complete. |
| Algebra | All students will: Plot the graph of quadratic equations Recognise quadratic,cubic and reciprocal graphs Solve simultaneous equations using equations and graphically |
Students will progress the more complex problems such as velocity/time graphs. They will also be able to solve quadratic simultaneous equations using substitution. | These units will be assessed using formative assessment whilst being delivered. Weekly homework on Sparx website, GCSE exam questions will be used within lessons. Post knowledge check will be used at the end of unit assessment, this will be marked by the student and teacher. The teacher will give feedback and set personalised task for the students to complete. |
| Statistics | All students will: Complete and interpret two way tables Plot various graphs such as cumulative frequency, histograms and box plots Identify misleading data from graphs Identify the components of effective sampling |
Students will be able to compare the distributions of cumulative frequency, histograms and box plots. Students who have mastered the topic will understand be able compare medians and interquartile ranges from box plots to cumulative frequency graphs and vice versa | These units will be assessed using formative assessment whilst being delivered. Weekly homework on Sparx website, GCSE exam questions will be used within lessons. Post knowledge check will be used at the end of unit assessment, this will be marked by the student and teacher. The teacher will give feedback and set personalised task for the students to complete. |
Summer Term
| What are we learning? | What knowledge, understanding and skills will we gain? | What will excellence look like? | How will we recognise progress? |
|
Higher
Circles arc lengths and sector areas circle theorems volume and surface area of circular shapes fractions indices standard form vectors and geometric proof constructions loci bearings
The students will also be preparing for their maths GCSE mock exams in the final half term of the year. |
Students will learn to calculate the area of a circle and sector, the circumference of a circle and the perimeter of a sector, including arc length. Students will learn the 8 circle theorems and the proofs of these, learning how to solve multiple step problems ensuring they can identify the reasons for the size of each angle. Students will learn how to use the formulae for volume and surface area of cylinders, spheres and cones. They will also look to solve volumes questions in algebra and in terms of pi.
Students will learn how to add, subtract, multiply and divide with fractions; this will also be within a real life context. Students will revisit multiplying and dividing with indices. Students will extend into simplifying fractional and negative indices. Students will recap how to convert between standard form and ordinary numbers and to solve problems with standard form.
Students will also look at how to solve geometric problems with vectors and how to prove vectors are parallel. Students will also learn how to use compasses and protractors to construct scale diagrams involving bearings and solve loci problems. |
Students with and excellent understanding of the topics this half term will be able to confidently choose the relevant methods and processes in order to answer questions confidently. Students will also show a strong knowledge of all formulae needed to calculate and solve multi-step problems which can occur within real life application. This may be using fractions within a sales context in shops or looking at how designers look to form 3D packaging to maximise volume. |
Knowledge and understanding will be assessed through homework tasks on SPARX maths, past GCSE paper questions, end of topic Post Knowledge checks. Half termly past paper assessment and Mock in Summer 2, teacher assessed and recorded centrally for monitoring of progress. Students will sit 3 maths papers for their mock exams in the final half term of the school year. The papers will be the same format as the GCSE exams they will be sitting next school year: 1 non-calculator paper followed by 2 calculator papers. Each exam will be 90mins in length. |
|
Foundation circles arc lengths and sector areas volume and surface area of circular shapes fractions indices standard form transformations constructions loci bearings
The students will also be preparing for their maths GCSE mock exams in the final half term of the year.
|
Students will learn to calculate the area of a circle and sector, the circumference of a circle and the perimeter of a sector, including arc length. Students will learn how to use the formulae for volume and surface area of cylinders, spheres and cones.
Students will learn how to add, subtract, multiply and divide with fractions; this will also be within a real life context. Students will revisit multiplying and dividing with indices. Students will learn how to convert between standard form and ordinary numbers and to solve problems with standard form.
Students will learn how to perform the following transformations: reflection, rotation, translation and enlargement. Students will learn to apply transformations to multi-step problems. Students will also learn how to use compasses and protractors to construct scale diagrams involving bearings and solve loci problems. |
Students with and excellent understanding of the topics this half term will be able to confidently choose the relevant methods and processes in order to answer questions confidently. Students will also show a strong knowledge of all formulae needed to calculate and solve multi-step problems which can occur within real life application. This may be using fractions within a sales context in shops or looking at how designers look to form 3D packaging to maximise volume. |
Knowledge and understanding will be assessed through homework tasks on SPARX maths, past GCSE paper questions end of topic Post Knowledge checks. Half termly past paper assessment and Mock in Summer 2, teacher assessed and recorded centrally for monitoring of progress. Students will sit 3 maths papers for their mock exams in the final half term of the school year. The papers will be the same format as the GCSE exams they will be sitting next school year: 1 non-calculator paper followed by 2 calculator papers. Each exam will be 90mins in length. |
Year 11 Curriculum Overview
Autumn Term
| What are we learning? | What knowledge, understanding and skills will we gain? | What will excellence look like? | How will we recognise progress? |
| Algebra |
Students will be preparing for their mock exams which will take place in October. The content of each class will be focused on Algebra with an individualised approach to what each class needs to study based on their year 10 mock analysis.
Topics that are to be included:
|
Confidence in applying skills in independent practise leading to problem solving skills with links to other areas of maths with a focus on geometry. |
These units will be assessed using formative assessment whilst being delivered. Weekly homework on Sparx website, GCSE exam questions will be used within lessons. Post knowledge check will be used at the end of unit assessment, this will be marked by the student and teacher. The teacher will give feedback and set personalised task for the students to complete. Students will be assessed via a formal maths mock assessment which will consist of 1 non-calculator paper and 2 non-calculator papers. Each paper will be 90mins long and will follow the syllabus of Edexcel Mathematics. |
Spring Term
| What are we learning? | What knowledge, understanding and skills will we gain? | What will excellence look like? | How will we recognise progress? |
| Gap analysis from mock exams | Students will be focusing on areas of weakness identified from their mock exams. This will be different for each class. | Confidence in applying skills in independent practise leading to problem solving skills with links to other areas of maths with a focus on geometry. | These units will be assessed using formative assessment whilst being delivered. Weekly homework on Sparx website, GCSE exam questions will be used within lessons. Post knowledge check will be used at the end of unit assessment, this will be marked by the student and teacher. The teacher will give feedback and set personalised task for the students to complete. |
| Geometry |
Foundation: Higher: |
Students will show excellence in learning through confidence in the manipulation of column vectors and use of vector notation to solve geometric problems. A strong understanding and use of circle theorems will be shown through solving multi-step exam problems with clear and concise reasoning shown. Students will confidently use trigonometry in 3D and use this to solve real life problems. | These units will be assessed using formative assessment whilst being delivered. Weekly homework on Sparx website, GCSE exam questions will be used within lessons. Post knowledge check will be used at the end of unit assessment, this will be marked by the student and teacher. The teacher will give feedback and set personalised task for the students to complete. |
| Number |
Foundation: Higher: |
Students will confidently manipulate percentage and worded proportion questions using a range of techniques including the use of reverse percentages and unitary proportion. Students will use their fluency of algebraic manipulation to solve and interpret direct and inverse proportion with confidence. Students will be familiar with formulae for speed, density and pressure and will manipulate these in order to solve problems, including changing units of length, area, volume and time. | These units will be assessed using formative assessment whilst being delivered. Weekly homework on Sparx website, GCSE exam questions will be used within lessons. Post knowledge check will be used at the end of unit assessment, this will be marked by the student and teacher. The teacher will give feedback and set personalised task for the students to complete. |
| In class mock exams |
All areas of maths to be addressed via 3 maths papers to be completed in class over 6 lessons, 45mins a lesson. |
Confidence in applying skills in independent practise leading to problem solving skills with links to other areas of maths with a focus on geometry. | Students will be assessed via a formal maths mock assessment which will consist of 1 non-calculator paper and 2 non-calculator papers. Each paper will be 90mins long and will follow the syllabus of Edexcel Mathematics |