ICT
Intent
Career Opportunities in ICT
The study of ICT & Computing allows you to develop skills that are well-suited to many different career choices. Some examples of careers you could pursue include website designer, systems analyst, game designer, network manager, software developer, systems engineer, ICT support, games developer, app developer, teacher, media assistant, cybersecurity specialist, artificial intelligence developer, and mobile technology developer. ICT & Computing fosters logical thinking skills, making it an excellent fit for any job involving problem-solving. Additionally, most office-based employment relies on ICT & Computing, and having a qualification in this field will open many doors for you.
ICT & Computing is recognized and valued by all employers and universities. The wide range of skills and knowledge fostered by the subject allows students to develop as individuals. Most universities offer courses in ICT & Computing, providing students with the opportunity for further development.
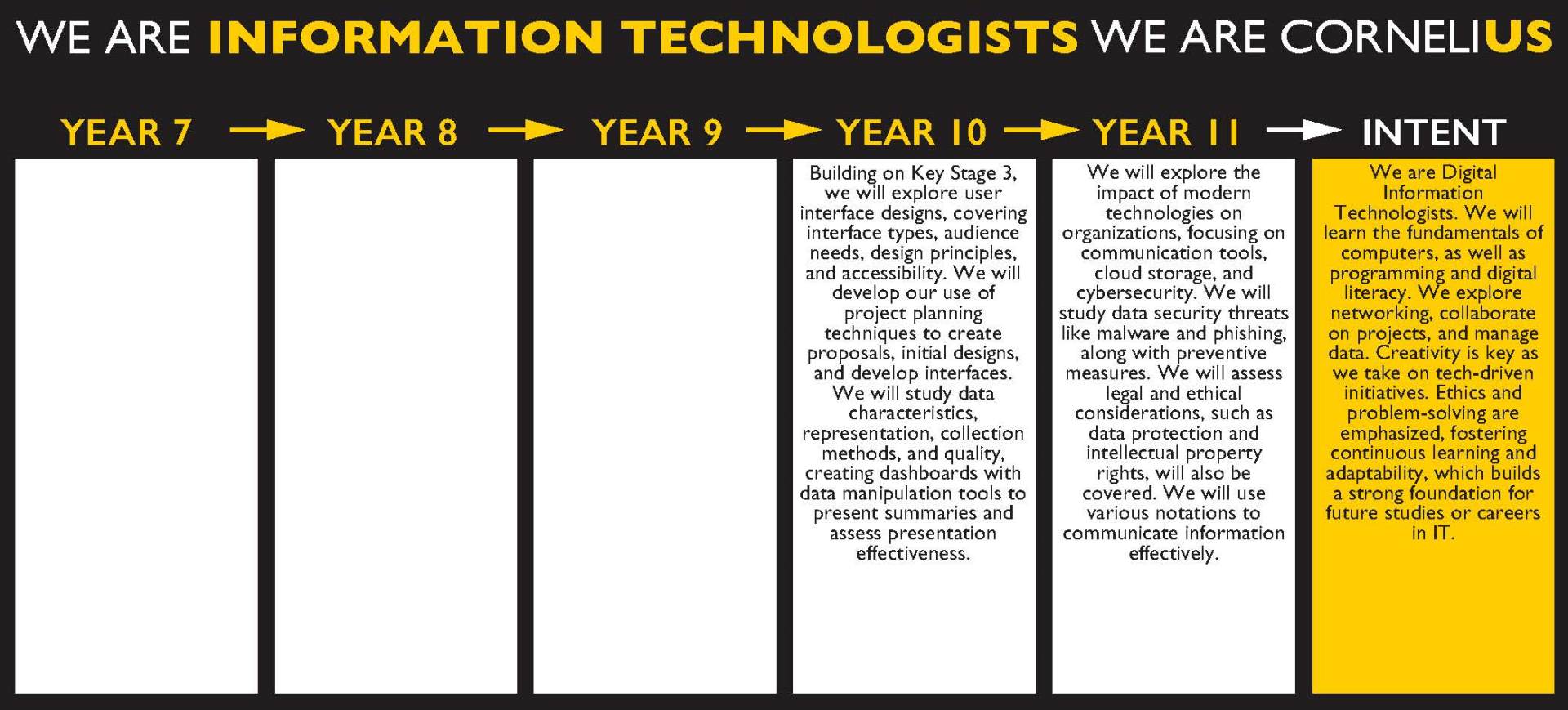
Year 10 Digital Information Technology Overview
Autumn
| What are we learning? | What knowledge, understanding and skills will we gain? | What will excellence look like? | How will we recognise progress? |
|
Exploring User Interface Design Principles and Project Planning techniques" |
Component 1: Learning Aim A:
Component 1: Learning Aim B:
Component 1: Learning Aim C
|
Students will develop their understanding of what makes an effective user interface and how to effectively manage a project. They will use this understanding to plan, design and create a user interface. Students will develop their knowledge and understanding of different project planning techniques that can be used to plan, develop and monitor projects. Learners will develop their knowledge and understanding of different user interface design principles. Learners will then be able to select appropriate project planning techniques to be able to plan and create an effective user interface that meets a set of defined user requirements. |
Through verbal Q and A in class. Practise of assignment based tasks. As the completed piece of coursework for component 1 – issued by exam board in September. |
Year 11 Digital Information Technology Overview
Autumn
| What are we learning? | What knowledge, understanding and skills will we gain? | What will excellence look like? | How will we recognise progress? |
| The wider implications of digital systems |
Environmental issues linked to business and personal use of computer systems, knowing the responsible disposal of old devices and systems – recycling centres, upgrading parts, safe disposal. Equal access - digital divide – between those that have/know the technology and those that don’t, what the impact is and how it can split society. Use policies within business structures – acceptable use, code of conduct etc. Data protection laws – the six elements of data handling and how business need to ensure they follow – implications if they do not. GDPR and data handling. |
I will be able to communicate what the various environmental issues are and explaining how the systems can be disposed / upgraded safely. I will be able to explain what equal access to digital systems is, and the groups that could feel marginalised by technology. I will be able to communicate what the data protection act covers, and how businesses can follow it – with implications if they do not. I will identify how GDPR has come in to play and what implications this has for Europe and data handling. |
Through verbal Q and A in class, worksheets working as a group or individual. As part of end of unit assessment that is exam based questions. |
|
Planning and communication in digital systems |
Data Flow diagrams – Information flow diagrams (IFD) and Data Flow Diagrams (level 0 and level 1) – the various symbols that create each diagram, and how we link them together with the rules for the diagram. Flow charts – basic structure and reasoning for flow charts, understating the need for a decision making process in them and how this forms looping mechanisms. |
Students will be able identify the differences between an IFD and a DFD, with clear knowledge of the components to each diagram. Students will be confident to create each chart for given scenario and apply logic for the construction of them.
Students will be able construct a flow chart and demonstrate understanding of decision making and implications for outcomes. |
Through verbal Q and A in class, worksheets working as a group or individual. As part of end of unit assessment that is exam based questions. |